

Understanding Reed Anatomy
A Guide for Woodwind Players and Educators
What is a Reed?

The reed is the heart of a woodwind instrument’s sound. Whether you’re playing clarinet or saxophone, understanding your reed’s structure is key to finding the right tone, response, and feel. Knowing the anatomy of a reed helps you choose the right reed for your playing style, adjust your setup for better tone and response, and diagnose issues like resistance, squeaks, or tonal flatness.
Reed Anatomy Breakdown
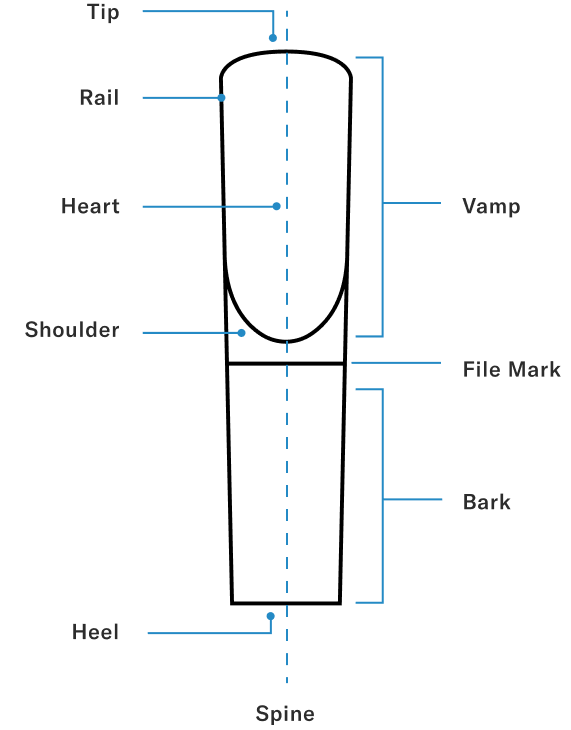
Tip
The tip of the reed is the thinnest and most flexible part of the reed. Thinner tips create quicker response, while thicker ones add resistance and tonal warmth.
Rail
The tip rails are the narrow edges flanking the reed’s tip that help center and guide its vibration, influencing quality and evenness of response
Heart
The heart is the thickest part of the vamp and is the reed’s central column of strength, shaping its tonal richness, resistance, and overall stability.
Spine
The central ridge that runs down the length of the reed. Adds structural integrity and influences projection.
Shoulder
The slope of a reed’s shoulders determines how quickly it responds to air and plays a key role in shaping its overall flexibility and tonal balance.
Heel
The heel, or "butt," is the thick, flat base of the reed that helps create a proper seal against the mouthpiece table; when warped or uneven, it can reduce the efficiency of the reed’s vibration and negatively affect tone and response.
File Mark
The boundary between the vamp and the bark/stock of the reed. Reeds can be filed or unfiled. Filed reeds have bark removed from the shoulders and can result in a more vibrant, responsive sound. Unfiled reeds leave some bark at the shoulders and results in added stability and tonal richness.
Vamp
The tapered section from tip to shoulders. The vamp's shape influences how the reed vibrates and determines it's overall character.
Bark / Stock
The uncut, bark-covered portion of the reed. Adds rigidity and affects how the reed seals to the mouthpiece. Sometimes the stock will be golden yellow and uniform in color, other times you will see gray/brown streaks. Both are completely normal.

Explore D’Addario Reeds
Whether you're a beginner or a pro, we offer reeds designed with precision and consistency in mind: from Reserve to Select Jazz and beyond.

